Open-Heart Surgery
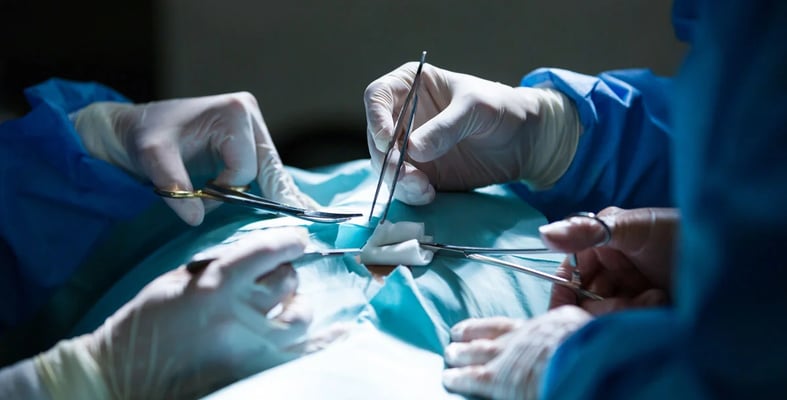
Open-heart surgery is a type of surgery in which the chest cavity is opened and a surgical procedure is performed on a part of the heart or its associated blood vessels.
Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) is by far the most commonly performed open-heart surgery, but there is a number of other cardiac surgical procedures that can be performed through open heart surgery technique.
What Are The Conditions That Open-Heart Surgery Treat?
Most of the time, cardiac surgeons perform open-heart surgery to make an arterial graft for coronary arteries that have stenosis (CABG). In this type of operation the heart surgeon needs to take an arterial or venous graft from elsewhere in the body such as the leg or chest, and this procedure is done for coronary artery patients who suffer from a partial or total blockage of their coronary arteries to a degree that cannot be treated with regular catheterization and stenting.
We also perform the following procedure using open-heart technique
- Heart valves repair and replacement
- Heart transplantation
- Cardiac defects repair
Before The Surgery
Your doctor will inquire about your medical and surgical history, the nature of chronic medical problems and diseases you have, such as hypertension, diabetes, and will also ask you about medications you use chronically, your surgeon will also perform a full physical exam.
After getting a thorough history and performing full physical examination, the surgeon will run some routine lab tests, such as blood tests, cholesterol level, among other tests related to the procedure to be done.
Our surgical team may also need one or more of the following investigations:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Echocardiogram (heart ultrasound)
- Diagnostic cardiac catheterization
- Chest x-rays
During Open-heart Surgery
Open-heart surgery is done under general anesthesia. During the operation the medical team follows up your vital signs such as blood pressure, heart rate, respiratory rate, and temperature, to make sure the surgery passes smoothly without complication, and to fix any problems that may arise in time.
Open-heart surgery takes approximately 3 to 6 hours, depending on the heart problem to be treated.
The surgeon makes a surgical incision in the middle of the chest, and the bones of the chest cage are opened in the middle to get into the chest cavity and get to operate on the heart.
After opening the chest cavity the surgeon stops the heart temporarily to be able to perform surgery on it, and in that time we use a special pump called the heart-lung bypass machine that takes over the heart pumping action while the heart is off. Sometimes the surgeon performs the operation on the heart without stopping it or needing a bypass machine, and that depends on the nature of the surgical problem and the doctor's judgement.
After Open-heart Surgery
The patient stays in the cardiac intensive care unit for one day, and is taken care of by a special critical care team to make sure that there are no postoperative problems, to control post-operative pain, and to prevent complications.

What Are The Risks Of Open-Heart Surgery?
The open heart surgery is a major surgery that is not without risks and potential complications. These risks may include:
- Surgical site infection and inflammation
- Anesthesia-related complications
- Heart rhythm disturbances
- Stroke
- Heart failure
These problems are rare and mostly happens in elderly patients, and most of these complications usually improves within 6 to 12 months after the procedure.
Do you have an inquiry? Contact us - For FREE Consultation.
Ilajak Medical© | A passion for care




Treatment Services
In the Best Medical Centers
Contact Us
Please fill the form below and describe your condition, We will contact you back
- Dental Treatment
- Hair Transplant
- Obesity Surgery
- Vision Correction
- Health Resorts
- Other Medical Services
- No elements found. Consider changing the search query.
- List is empty.
Your personal data is processed as indicated in the general statement text and by continuing, you explicitly consent to the processing

